WHO FAVORS a two-state solution to the Arab-Israeli conflict?
 President Obama and Prime Minister Netanyahu converse in the Oval Office (May 18, 2009) |
Pope Benedict XVI called for a Palestinian state during his recent visit to the Holy Land, thereby aligning himself -- on this issue, at least -- with the editorial boards of The New York Times, The Boston Globe, The Washington Post, and The Los Angeles Times. And, for that matter, with most Israelis. A new poll shows 58 percent of the Israeli public backing a two-state solution; prominent supporters include Netanyahu's three predecessors -- former prime ministers Ehud Olmert, Ariel Sharon, and Ehud Barak -- as well as president Shimon Peres.
The consensus, it would seem, is overwhelming. As Henri Guaino, a senior adviser to French President Nicolas Sarkozy, put it in speaking to reporters on Sunday: "Everyone wants peace. The whole world wants a Palestinian state."
It isn't going to happen.
International consensus or no, the two-state solution is a chimera. Peace will not be achieved by granting sovereignty to the Palestinians, because Palestinian sovereignty has never been the Arabs' goal. Time and time again, a two-state solution has been proposed. Time and time again, the Arabs have turned it down.
In 1936, when Palestine was still under British rule, a royal commission headed by Lord Peel was sent to investigate the steadily worsening Arab violence. After a detailed inquiry, the Peel Commission concluded that "an irrepressible conflict has arisen between two national communities within the narrow bounds of one small country." It recommended a two-state solution -- a partition of the land into separate Arab and Jewish states. "Partition offers a chance of ultimate peace," the commission reported. "No other plan does."
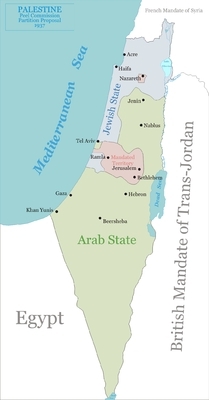 The Peel Commission's proposed two-state solution (1937). The Arabs said no. |
In 1947, the Palestinians were again presented with a two-state proposal. Again they spurned it. Like the Peel Commission, the United Nations concluded that only a division of the land into adjacent states, one Arab and one Jewish, could put an end to the conflict. On Nov. 29, 1947, the UN General Assembly debated -- and by a vote of 33-13 adopted -- Resolution 181, partitioning Palestine on the basis of population. Had the Arabs accepted the UN decision, the Palestinian state that "the whole world wants" would today be 61 years old. Instead, the Arab League vowed to block Jewish sovereignty by waging "a war of extermination and a momentous massacre."
Over and over this pattern has been repeated. Following its stunning victory in the 1967 Six Day War, Israel offered to exchange the land it had won for permanent peace with its neighbors. From their summit in Khartoum came the Arabs' notorious response: "No peace with Israel, no negotiations with Israel, no recognition of Israel."
At Camp David in 2000, Ehud Barak offered the Palestinians virtually everything they claimed to be seeking -- a sovereign state with its capital in East Jerusalem, 97 percent of the West Bank and Gaza Strip, tens of billions of dollars in "compensation" for the plight of Palestinian refugees. Yasser Arafat refused the offer, and launched the bloodiest wave of terrorism in Israel's history.
To this day, the charters of Hamas and Fatah, the two main Palestinian factions, call for Israel's liquidation. "The whole world" may want peace and a Palestinian state, but the Palestinians want something very different. Until that changes, there is no two-state solution.
(Jeff Jacoby is a columnist for The Boston Globe.)

